Insight Blog
Agility’s perspectives on transforming the employee's experience throughout remote transformation using connected enterprise tools.
17 minutes reading time
(3459 words)
Building Transient Advantage Using AI - A Complete Guide
Explore how AI fosters transient advantage in business, emphasizing agility and innovation for competitive success.
Transient advantage is now the primary factor for business success in the dynamic and volatile business environment where the main objective is to keep the competitive edge. While markets change and technology matures, the one thing that makes or breaks a company is the speed at which it can adjust and innovate, to survive and expand.
This notion of transitory advantage encompasses temporary competitive gains that need to be perpetually renewed.
This idea is especially relevant in the age of artificial intelligence (AI). AI is not only a change accelerator, it is also an enabler of a company's swiftness in navigating through competitive landscapes by using data-driven insights and automating the complex processes.
What is Transient Advantage?
Transient advantage in business refers to a strategic approach where companies continually seek, capture, and exploit temporary opportunities to gain competitive edges in rapidly changing markets. Unlike sustained competitive advantages, which companies maintain over long periods, transient advantages are short-lived, requiring firms to be agile and ready to move on to the next opportunity. This concept recognizes the dynamic nature of modern business landscapes, where long-term success depends on flexibility and the ability to innovate continually.
Transient advantage meaning is a competitive edge that lasts for a short period. This strategy acknowledges the fast-paced nature of business today, where things can change quickly.
Here are some critical points about transient advantage:
- Focuses on constant innovation: Companies that adopt this strategy don't rely on one significant advantage for a long time. Instead, they're constantly looking for new ways to be innovative and stay ahead of the competition.
- Adapts to change: The idea is to be agile and adaptable to changing market conditions and customer needs.
- Shorter advantage cycles: Transient advantages are expected to be temporary, so companies need to be quick at identifying new opportunities, exploiting them, and then moving on to the next one.
This approach is becoming increasingly important as globalization and digital disruption make sustaining a long-lasting competitive edge harder.
- Price Discounts: Offering temporary discounts or promotions can attract customers in the short term. However, customers may revert to competitors offering similar products at regular prices once the promotion ends.
- Limited-Time Offers: Limited-time offers or flash sales can create a sense of urgency and drive immediate sales spikes. However, the advantage dissipates once the offer period expires, and customers may seek alternatives.
- Exclusive Partnerships: Securing exclusive partnerships or distribution agreements can provide a temporary advantage by limiting competitors' access to particular products or markets. However, the advantage diminishes once the exclusivity period ends or competitors find alternative routes.
- First-Mover Advantage: Being the first to market with a new product or innovation can yield initial success as competitors play catch-up. However, the advantage erodes as competitors enter the market with similar offerings or improvements.
- Seasonal Trends: Capitalizing on seasonal trends or fads can generate significant sales during peak periods. However, the advantage fades once the trend subsides or shifts, and businesses must adapt to new consumer preferences.
- Technology Advancements: Leveraging cutting-edge technology or features in products can temporarily differentiate a business. However, as technology evolves rapidly, competitors may quickly replicate or surpass these advancements, diminishing the advantage.
- Brand Hype: Creating a buzz around a new brand or product launch can generate initial excitement and sales. However, sustaining long-term brand loyalty requires consistent value delivery and customer satisfaction beyond the initial hype.
Here are a list examples of transient advantage strategy
Several companies have effectively employed a transient advantage strategy to stay ahead in their respective industries, we have provide a list examples of transient advantage strategy:
- Apple stands out as a prime example of leveraging innovation to maintain a competitive edge. Renowned for its continuous stream of groundbreaking products, such as the iPhone with its pioneering touchscreen interface, Apple demonstrates how introducing novel features can secure a temporary advantage in the market.
- Amazon's success story is built on adaptability and a relentless focus on customer satisfaction. Early innovations like one-click ordering and speedy delivery were instrumental in establishing Amazon as a dominant force in online retail. By continuously evolving and meeting customer needs, Amazon has consistently stayed ahead of the curve.
- Fast fashion brands have mastered the art of capitalizing on fleeting trends. By swiftly identifying and delivering the latest styles at affordable prices, these brands secure a transient advantage, attracting customers seeking the latest fashion fix before trends shift. This ability to quickly respond to changing consumer preferences allows fast fashion brands to carve out a niche in the market and stay relevant amidst evolving fashion trends.
Transient competitive advantage examples
Transient competitive advantages represent brief periods of superiority that propel a company ahead in the marketplace.
Here are some notable instances:
Southwest Airlines' strategic focus on short-haul flights between smaller airports granted them a sustained advantage, as larger carriers struggled to match their efficiency on these routes. This niche strategy allowed Southwest to dominate the market for years, showcasing the power of targeted specialization.
Dell revolutionized the computer industry with its pioneering approach to mass customization. By offering PCs tailored to individual customer specifications, Dell gained a significant edge over competitors, attracting customers seeking personalized computing solutions. This bespoke model catapulted Dell to prominence in the tech world.
However, these advantages are fleeting, susceptible to erosion from competitive forces or shifts in the market landscape. Yet, they afford companies crucial breathing space to solidify their position and strategize for the future.
Consider Kodak's foray into digital photography—a potential game-changer that could have provided a transient advantage. Kodak's invention of the digital camera positioned them at the forefront of innovation in imaging technology. However, their failure to pivot effectively and transition from traditional film-based products ultimately led to their downfall. Kodak's story serves as a cautionary tale, highlighting the importance of adapting alongside transient advantages to remain relevant in a rapidly evolving market.
Follow us and access great exclusive content everyday: Follow us on Google News
AI's Role in Enabling Transient Advantages
AI is dramatically transforming competitive landscapes by enabling businesses to capitalize on transient advantages more effectively.
AI technologies enhance the speed and accuracy of data analysis, allowing companies to quickly identify and act upon emerging trends and operational efficiencies. Companies can also use AI to train their employees. For example, AI-driven analytics can pinpoint shifting consumer preferences, while AI-enhanced automation streamlines production processes, both critical in rapidly seizing and exploiting market opportunities.
AI facilitates personalized customer experiences and predictive decision-making, empowering businesses to stay ahead in the competition by continually adapting to new challenges and opportunities.
Understanding Rita McGrath's Transient Advantage
You may also like: Best Apps for Employees: UPDATED 2022 – A Complete Guide
Rita McGrath's Concept of Transient Advantage
Rita McGrath Transient Advantage theory revolutionizes the traditional understanding of strategic planning in business.
McGrath argues that in a fast-changing environment, competitive advantages are often transient rather than permanent. She suggests that businesses should not seek to develop sustainable advantages as a long-term goal but should instead focus on capitalizing on fleeting opportunities. This approach requires companies to be perpetually innovative and agile, quickly adapting to changes and discontinuities in the market.
McGrath emphasizes the importance of constantly reconfiguring and reinventing business strategies to gain short-lived competitive edges that can lead to significant growth and profitability before they dissipate.
Key Characteristics of Transient Advantage
The key characteristics of transient advantage include market instability and rapid technological change, which necessitate continuous adaptation and strategic innovation. First, transient advantages are short-lived, as they quickly become obsolete or are replicated by competitors. Therefore, companies must continuously seek new advantages.
Second, this approach favors agility over stability, encouraging businesses to remain flexible and responsive to market changes rather than heavily investing in long-term planning. Third, McGrath points out the importance of disengagement; companies must be ready to exit strategies that are no longer profitable and shift resources to more promising areas.
Lastly, transient advantage thrives in an environment that supports rapid experimentation and failure, fostering a culture where quick trials and learning from mistakes are seen as stepping stones to discovering new competitive advantages.
Free ebook: How To Get Your Intranet Off The Ground
Building Transient Competitive Advantage in Business
Strategies for Building Transient Advantage Using AI Technologies
Transient competitive advantage can be significantly enhanced through the strategic deployment of AI technologies.
One effective strategy is the utilization of machine learning models to predict market trends and customer behaviors, allowing businesses to anticipate and react to changes faster than competitors. Another strategy involves the use of AI for optimizing supply chains and logistics, ensuring that businesses can adapt their operations dynamically to meet changing market demands.
Additionally, implementing AI-driven automation can enhance product innovation cycles, enabling companies to frequently introduce new, tailored offerings that meet niche market needs and thus capture transient advantages.
Importance of Agility, Innovation, and Customer-Centric Approaches
In today's fast-paced market environment, the importance of agility, innovation, and customer-centric approaches cannot be overstated in securing transient competitive advantages. Agility allows businesses to pivot quickly in response to market changes, while a strong focus on innovation helps in continuously generating fresh ideas that can lead to new opportunities.
Adopting a customer-centric approach ensures that innovations and business adjustments are aligned with evolving customer needs and expectations, which is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in markets where customer preferences change rapidly.
How AI Contributes to These Strategies
AI significantly bolsters the strategies of agility, innovation, and customer-centricity.
By leveraging data analytics and predictive modeling, AI provides businesses with insights that enhance decision-making and strategic pivots in real-time, embodying agility. For innovation, AI tools can help in the rapid development of products and services by streamlining R&D processes through automation and simulation technologies.
AI enhances customer-centric approaches through personalized marketing and customer service bots that deliver tailored experiences and gather valuable feedback directly from users, fostering a direct connection and ongoing adaptation to customer needs and preferences.
Transient Advantage Examples
Transient advantage examples in business are often highlighted due to their temporary assistance that companies can use to get ahead of competition.
E-Commerce
Amazon adapts its prices using AI mechanisms in order to be more attractive by providing the best deals to customers in real-time. With the help of A.I, Amazon can offer a short-term edge during popular shopping periods when shoppers are most likely to be sensitive to price, such as on Black Friday or holidays.
While serving the customer, Alibaba and JD.com employ AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants that use customer inquiries and behavior data to give personalized guidance and promotional offers. It not only leads to the betterment of the shopping experience but also can help a lot in the increasing of sales by making the most of the instantaneous benefits of the close and direct interaction with the consumers and the tailored marketing.
Finance Sector
AI algorithms in the finance sector are applied by investment companies to accomplish high-frequency trading, which is based on algorithms.
These algorithms perform lightning analysis on the market data and make trades that exploit the micro-inefficiencies in the market in a matter of seconds. This has a temporary effect as the steps are taken to gain a competitive edge in the market in which there is a short time to capture the opportunity before the market conditions change.
Car Market
For example, in the car market, Tesla uses AI to enable the auto-upgrading of the software of its vehicle, online.
This not only increases the feature set of vehicles with performance and functionality that may not exist in competitors' products, but also leads to higher customer satisfaction and retention. This just results in a temporary competitive advantage for almost any market in the automotive market.
Sustainable Competitive Advantage vs. Transient Advantage
Comparison of Sustainable and Transient Competitive Advantages
Sustainable competitive advantage vs transient advantage represents two distinct strategic approaches in business. Sustainable competitive advantage is achieved when a company maintains a superior position over its competitors for a prolonged period through resources and capabilities that are difficult to imitate. Examples include brand reputation, proprietary technology, or unique business processes.
On the other hand, transient advantage focuses on exploiting short-lived opportunities in a fast-paced and ever-changing environment. This approach requires continual innovation and rapid response to market changes, rather than relying on long-term stability.
Why and When Businesses Might Prefer One Over the Other
Businesses might prefer sustainable competitive advantage in stable industries where the pace of change is slow, and investments in long-term assets such as brand development or patented technologies can yield extended benefits. In contrast, in industries characterized by rapid technological advancements and changing consumer preferences, transient advantage is more suitable.
Here, the ability to quickly adapt and innovate is crucial. Companies in tech, fashion, or consumer electronics, where new trends and technologies constantly emerge, often benefit from this approach by regularly introducing new products and services to meet the latest demands.
The Evolving Nature of Business Strategies
The nature of business strategies is evolving from a focus on building sustainable advantages to recognizing the value of transient advantages.
This shift is largely driven by the acceleration of technological change, globalization, and dynamic market conditions. Modern businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid strategies that blend stability with agility, embedding flexibility in their long-term planning to allow for adjustments as market conditions dictate. This evolution reflects an understanding that competitive advantage is no longer a static goal but a fluid objective that requires continuous reassessment and adaptation.
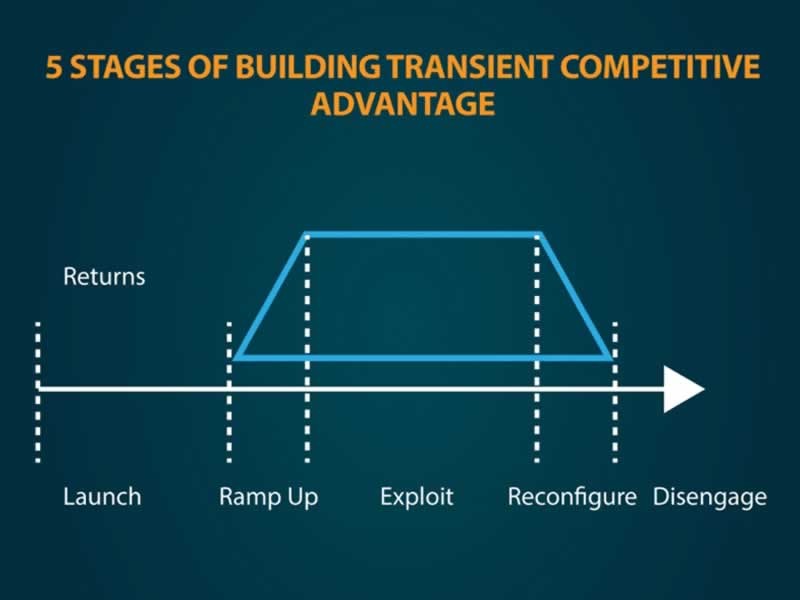
How to Build Transient Competitive Advantage
Crafting a transient competitive advantage involves navigating five crucial stages:
- Launch: Begin by identifying a unique opportunity or innovative concept that can provide a temporary edge in the market. This could involve introducing a new product, service, or business model that addresses unmet needs or disrupts existing norms.
- Ramp Up: Once the initial idea is conceptualized, dedicate resources to scale up operations and establish a strong presence in the market. This phase may involve intensive research and development, marketing campaigns, and strategic partnerships to amplify the advantage and gain traction.
- Exploit: With momentum building, leverage the advantage to its fullest potential. Capitalize on the uniqueness of the offering to capture market share, attract customers, and outmaneuver competitors. This phase is where the advantage shines brightest, driving growth and profitability.
- Reconfigure: As competitors inevitably catch up or market dynamics shift, be prepared to adapt and evolve. Reconfigure the advantage by refining existing strategies, exploring new markets, or innovating further to sustain relevance and prolong the advantage's lifespan.
- Disengage: Recognize when the advantage has run its course and it's time to exit or pivot to new opportunities gracefully. Disengagement doesn't necessarily mean abandoning the market but rather strategically reallocating resources to other areas where a fresh advantage can be cultivated.
Strategic decisions and actions play a pivotal role in each stage of building a transient competitive advantage. Effective leadership, market intelligence, and agility are essential ingredients for success. Additionally, fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement within the organization can facilitate identifying new opportunities and adapting quickly to changing circumstances.
Most importantly, sustaining a transient advantage requires a keen awareness of external factors such as technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and competitive landscape dynamics. Companies must remain vigilant and proactive in monitoring these factors to stay ahead of the curve and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Also, collaboration with external partners, including suppliers, distributors, and industry experts, can provide valuable insights and resources to enhance the advantage further. Strategic alliances and joint ventures can also bolster capabilities and broaden market reach, contributing to the overall success of the transient advantage strategy.
Ultimately, the ability to build and capitalize on transient competitive advantages is a dynamic process that demands creativity, resilience, and strategic foresight. Companies can position themselves for sustained success in an ever-evolving marketplace by mastering these stages and continually refining their approach.
Transient competitive advantage in strategic management
So lets get in to transient benefit in strategic management, a transient competitive advantage refers to a company's temporary edge over its competitors. Unlike sustained, more durable, long-lasting competitive advantages, transient advantages are typically short-lived. They may arise from technological breakthroughs, market shifts, or temporary inefficiencies in the competitive landscape.
Companies often strive to leverage transient advantages to gain market share, increase profitability, or achieve specific strategic objectives. However, because these advantages are temporary, they require vigilant monitoring and rapid exploitation to extract maximum value before dissipating.
Examples of transient competitive advantages include:
- First-mover advantage: The first to enter a new market or introduce a new product can provide a temporary edge as competitors scramble to catch up.
- Exclusive partnerships or contracts: Securing exclusive agreements with suppliers, distributors, or strategic partners can temporarily limit competitors' access to critical resources or markets.
- Technological innovation: Introducing a new technology or innovation that temporarily outpaces competitors can provide a short-term advantage until others replicate or improve upon the innovation.
- Market trends and fads: Capitalizing on short-lived consumer trends or fads can temporarily boost sales and market share.
- Regulatory changes: Adapting quickly to regulatory changes or exploiting regulatory loopholes can provide a temporary advantage until competitors catch up or regulations are further amended.
Transient competitive advantages are significant in strategic management because they can provide opportunities for companies to create value, differentiate themselves, or disrupt existing markets. However, relying solely on transient advantages without developing sustainable capabilities can leave companies vulnerable once the advantage dissipates. Therefore, effective strategic management involves balancing exploiting transient advantages with developing sustained competitive capabilities.
So Which Companies Have Adopted Transient Competitive Advantage
Several companies across various industries have leveraged transient competitive advantages to achieve short-term success.
Here are a few examples:
- Apple Inc.: Apple has a history of leveraging transient competitive advantages through its innovative product launches. For instance, introducing the iPhone created a significant first-mover advantage in the smartphone market, driving rapid sales growth and market dominance. Subsequent iPhone releases continued to capitalize on technological advancements and consumer trends, maintaining Apple's transient advantage in the smartphone industry.
- Uber disrupted the traditional taxi industry by leveraging a transient competitive advantage based on technological innovation and changing consumer preferences. Its mobile app provided a convenient and efficient alternative to conventional taxis, quickly gaining market share and valuation. However, Uber's advantage has faced challenges from regulatory issues, competition, and evolving consumer preferences, highlighting the transient nature of its competitive edge.
- Netflix: Netflix capitalized on the shift from traditional cable TV to streaming services by offering a vast library of on-demand content at competitive prices. This transient competitive advantage was driven by changing consumer preferences for on-demand, personalized entertainment. However, as more competitors entered the streaming market and content licensing became more competitive, Netflix's advantage became less pronounced, emphasizing the transient nature of its competitive edge.
- Tesla: Tesla's early dominance in the electric vehicle (EV) market provided a transient competitive advantage fueled by its innovative technology, brand appeal, and visionary leadership. However, as traditional automakers and new entrants invested heavily in EV technology, Tesla's advantage has become increasingly challenged. Its ability to maintain market leadership will depend on its ability to sustain innovation and adapt to evolving market dynamics.
- Airbnb disrupted the hospitality industry by leveraging a transient competitive advantage based on the sharing economy and changing travel preferences. Its platform enabled homeowners to monetize their properties as short-term rentals, appealing to budget-conscious travelers seeking unique accommodations. However, Airbnb's advantage has faced challenges from regulatory issues, competition, and consumer behavior shifts, highlighting its competitive edge's transient nature.
These examples illustrate how companies can achieve short-term success by capitalizing on transient competitive advantages. However, sustaining long-term success requires companies to adapt to changing market dynamics, innovate continuously, and develop sustainable competitive capabilities.
Wrapping up
Mastering transient advantage through AI and strategic agility is becoming essential in today's competitive business landscape. As markets continue to evolve at an unprecedented rate, the ability to swiftly adapt and exploit fleeting opportunities can dictate a company's success. This approach, highlighted by Rita McGrath's concept of transient advantage, encourages continuous innovation and responsiveness.
Businesses must integrate AI technologies to stay relevant and maneuver quickly in dynamic environments, blending the pursuit of transient and sustainable advantages to navigate both short-term opportunities and long-term challenges effectively.
Categories
Blog
(2720)
Business Management
(333)
Employee Engagement
(213)
Digital Transformation
(185)
Growth
(124)
Intranets
(120)
Remote Work
(61)
Sales
(48)
Collaboration
(43)
Culture
(29)
Project management
(29)
Customer Experience
(26)
Knowledge Management
(21)
Leadership
(20)
Comparisons
(8)
News
(1)
Ready to learn more? 👍
One platform to optimize, manage and track all of your teams. Your new digital workplace is a click away. 🚀
Free for 14 days, no credit card required.