Insight Blog
Agility’s perspectives on transforming the employee's experience throughout remote transformation using connected enterprise tools.
12 minutes reading time
(2368 words)
Manipulative Insincerity - What Is It & How It Impacts Organizations?
Explore the impact of manipulative insincerity in organizations and strategies to foster a culture of honesty and transparency.
Manipulative insincerity, a nuanced yet detrimental phenomenon, often pervades organizational cultures, subtly undermining their integrity and efficiency.
This deceptive practice, marked by dishonesty and a lack of genuine intent, poses significant challenges in the workplace, leading to a cascade of negative impacts.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the essence of manipulative insincerity, dissecting its characteristics, origins, and the profound implications it has on organizational communication and feedback. Additionally, we will explore strategies, like Radical Candor, designed to counteract its pervasive effects.
Understanding and addressing manipulative insincerity is crucial for fostering a culture of transparency and trust, essential for any thriving organization.
Manipulative Insincerity - A Complete Guide
What Is Manipulative Insincerity?
Manipulative insincerity is a complex term that encapsulates a range of deceptive interpersonal behaviors within organizational contexts.
Characterized by a lack of authenticity, this behavior involves individuals conveying messages or feedback that are neither honest nor genuine. Often, this insincerity stems from a desire to avoid conflict, gain personal advantage, or maintain a certain image.
Unlike straightforward dishonesty, manipulative insincerity is subtler, blending elements of truth with misleading intentions.
Key characteristics include a disingenuous demeanor, where the person's words do not align with their true thoughts or feelings. This can manifest in excessive flattery, ambiguous or non-committal language, and avoidance of direct confrontation or difficult conversations.
Such behavior not only hinders clear communication but also fosters an environment of mistrust and skepticism. Recognizing and understanding these traits is vital for identifying manipulative insincerity and addressing its corrosive impact on organizational culture.
Examples of Manipulative Insincerity
Manipulative insincerity refers to behavior that lacks both honesty and kindness. It involves saying or doing things with insincere intentions, often aimed at achieving personal goals.
Here are several examples:
- Backhanded compliments: These are disguised insults presented as praise. For instance, saying, "You look great for your age," or "I'm impressed you can tie your own shoes," intends to make the recipient feel insecure or inferior.
- False promises: Manipulative individuals often make commitments they have no intention of fulfilling. From promises to assist with projects to offering emotional support, broken promises can erode trust and strain relationships.
- Guilt trips: This tactic involves making someone feel guilty to manipulate them into doing what the manipulator desires. Statements like, "You're so selfish," or "I can't believe you would do this to me after everything I've done for you," are attempts to leverage guilt for compliance. It's crucial to recognize that you are not responsible for others' feelings.
- Playing the victim: Manipulative individuals portray themselves as victims, even if they are at fault. This may involve exaggerating the other person's actions or downplaying their own role in a conflict.
- Gaslighting: Gaslighting is a form of emotional abuse where someone undermines your perception of reality. This can include denying past statements or actions, or convincing you that your thoughts are imaginary. Gaslighting can have severe impacts on mental health, and recognizing the signs is essential.
If you find yourself being manipulated, it's crucial to establish boundaries and assert yourself. You do not have to endure unfair treatment. Numerous resources, such as books, websites, and hotlines, are available to help individuals dealing with manipulative behavior.
It's important to note that manipulative insincerity can be subtle, making it challenging to detect initially. By staying vigilant and recognizing the signs, you can safeguard yourself from being taken advantage of.
Contrasting Manipulative Insincerity with Genuine Behavior
Manipulative insincerity and genuine behavior represent two distinct ends of the interpersonal spectrum in organizational contexts. Genuine behavior is rooted in honesty and authenticity. It involves open, transparent communication where individuals express their true thoughts and feelings without hidden agendas. This sincerity fosters trust and strengthens relationships, as colleagues feel confident that they are receiving honest feedback and information.
In stark contrast, manipulative insincerity is characterized by a façade of agreement or support, masking true intentions or feelings. This duplicity often serves self-interests, leading to misleading or incomplete communication. It erodes trust, as colleagues begin to question the veracity of the interactions they engage in.
The key difference lies in the intent and transparency of the communication. While genuine behavior aims to build mutual understanding and respect, manipulative insincerity seeks to deceive or gain an advantage, often at the expense of others. Recognizing this distinction is crucial for nurturing a healthy, transparent, and effective organizational environment.
The Psychological Underpinnings of Manipulative Insincerity
The psychological underpinnings of manipulative insincerity are multifaceted, often rooted in deep-seated fears, insecurities, and self-interest. At its core, this behavior can be driven by a fear of conflict or negative repercussions.
Individuals may resort to insincerity to avoid confrontation, believing that disguising their true thoughts or feelings will maintain harmony or protect their self-image.
Another factor is the desire for personal gain or advancement. In competitive work environments, individuals might employ manipulative tactics to outmaneuver colleagues, curry favor with superiors, or secure personal benefits. This behavior is underpinned by a belief that genuine honesty may not yield the desired outcomes, leading to a preference for manipulation over transparency.
Furthermore, psychological factors such as low self-esteem or a lack of emotional intelligence can contribute to manipulative behavior.
Individuals with low self-esteem might feel incapable of withstanding the potential fallout of honest interactions, while those lacking emotional intelligence may struggle to navigate complex interpersonal dynamics effectively.
Lastly, organizational culture plays a significant role. In environments where honesty is not valued or where there is a lack of psychological safety, manipulative insincerity can become a survival mechanism.
Understanding these psychological motivations is critical in addressing manipulative behavior and fostering a culture of sincerity and trust within organizations.
Follow us and access great exclusive content everyday: Follow us on Google News
Radical Candor for Manipulative Insincerity
Radical Candor Manipulative Insincerity emerge as a transformative communication philosophy.
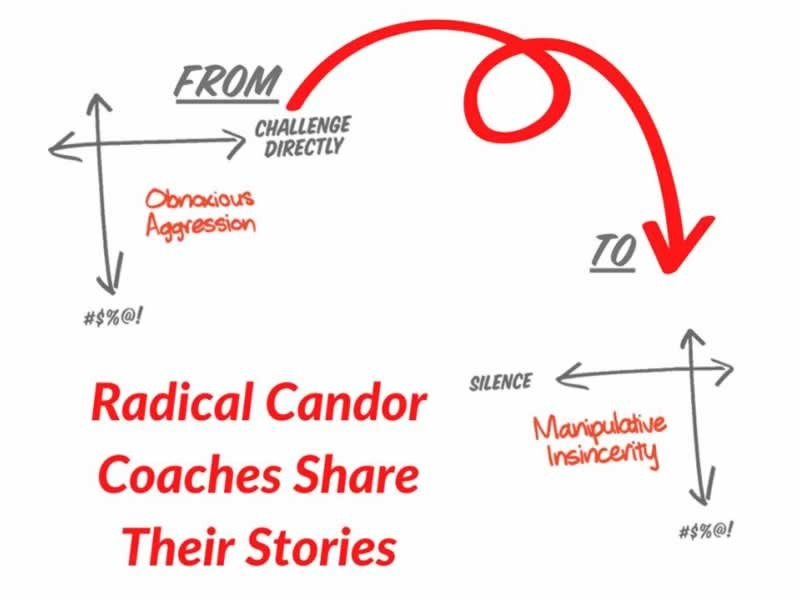
Developed by Kim Scott, Radical Candor is a framework designed to foster open, honest, and caring communication in professional settings. Its foundational principle is to care personally while challenging directly, advocating for interactions that are both empathetic and straightforward.
This method encourages leaders and team members to provide direct feedback, delivered with a genuine concern for personal growth and team success.
Central to Radical Candor are two key dimensions, namely "Care Personally" and "Challenge Directly." "Care Personally" involves showing genuine interest and concern for team members, recognizing them as individuals with unique aspirations and challenges. "Challenge Directly," on the other hand, emphasizes the importance of honest, clear feedback, even when it might be uncomfortable. By combining these dimensions, Radical Candor enables a productive dialogue where feedback is both respectful and constructively critical.
This approach stands in stark contrast to Manipulative Insincerity, where feedback is often misleading or withheld to avoid discomfort or gain advantage.
Adopting Radical Candor can thus be a powerful antidote to the toxic effects of manipulative behaviors in the workplace.
Applying Radical Candor to Counteract Manipulative Insincerity
Applying Radical Candor in environments plagued by Manipulative Insincerity involves several strategic steps. The first step is fostering a culture of open communication. Leaders must lead by example, showing vulnerability and honesty in their interactions. This sets a precedent, encouraging team members to express their thoughts and concerns without fear of retribution.
Secondly, regular, structured feedback sessions are crucial. These sessions, grounded in the principles of Radical Candor, should be designed to provide clear, actionable feedback. Encouraging a two-way dialogue ensures that feedback isn't just given but also received, fostering a sense of mutual respect and understanding.
Thirdly, training sessions can be instrumental in educating employees about the benefits of Radical Candor versus the pitfalls of Manipulative Insincerity. These sessions should include practical exercises that help participants understand how to apply Radical Candor in real-world scenarios.
Another effective strategy is the establishment of clear communication guidelines. These guidelines should emphasize the importance of direct but empathetic communication, offering a framework that discourages manipulative behaviors.
Lastly, it's important to recognize and reward instances of Radical Candor.
This positive reinforcement can shift the organizational mindset, gradually phasing out manipulative behaviors. Over time, these strategies can transform an environment tainted by insincerity into one where honest, constructive communication is the norm, fostering a healthier, more productive organizational culture.
You may also like: Best Apps for Employees: UPDATED 2022 – A Complete Guide
Challenges in Implementing Radical Candor
Implementing Radical Candor in organizations often encounters significant challenges. A primary difficulty is overcoming ingrained cultural norms, especially in environments where indirect communication or hierarchical structures have long been the status quo.
In such settings, shifting to a culture of openness and direct feedback can be met with resistance, discomfort, and skepticism.
Another challenge lies in balancing the 'caring personally' and 'challenging directly' aspects.
Some employees may struggle with being direct in their feedback for fear of offending others, while others might lean too heavily on directness, coming across as abrasive or insensitive. Finding the right balance requires nuanced understanding and practice, and missteps can lead to misunderstandings or resentment.
Additionally, leaders may face difficulties in ensuring consistency in the application of Radical Candor across all levels of the organization. Inconsistencies in how managers apply these principles can lead to confusion and a lack of trust in the system.
Lastly, time constraints in fast-paced work environments can hinder the regular, thoughtful interactions necessary for Radical Candor. Prioritizing these conversations and embedding them into the fabric of organizational processes is essential yet challenging, requiring a concerted effort from all members of the organization.
How Manipulative Insincerity Leads To Bad Feedback?
Manipulative Insincerity and bad feedback are about distorting the quality of communication within organizations.
This insincerity, marked by a lack of honesty and transparency, results in feedback that is either misleading or so diluted that its value is lost.
Such feedback fails to provide clear direction or constructive criticism, hindering personal and professional development.
Free ebook: How To Get Your Intranet Off The Ground
Impact on Organizational Communication up
Manipulative Insincerity often leads to bad feedback, fundamentally distorting the quality of communication within organizations.
This insincerity, marked by a lack of honesty and transparency, results in feedback that is either misleading or so diluted that its value is lost. Such feedback fails to provide clear direction or constructive criticism, hindering personal and professional development.
In an environment where manipulative insincerity prevails, there is a tendency to avoid addressing problems directly. This leads to a culture where issues are swept under the rug rather than being resolved, allowing them to fester and potentially worsen.
The absence of honest feedback creates blind spots, where employees and leaders are unaware of areas needing improvement.
Furthermore, manipulative insincerity can breed a culture of mistrust. When feedback is not given with genuine intent, employees begin to question the motives behind it.
This skepticism can lead to a breakdown in communication channels, as employees may withhold information, ideas, or concerns, fearing that open communication will not be received positively or could be used against them.
In such an environment, decision-making becomes impaired. Without accurate and honest feedback, leaders cannot make informed decisions, and employees are left without the guidance needed to perform effectively.
Over time, this can lead to decreased morale, engagement, and productivity, significantly impacting the organization's overall performance.
Case Studies of Poor Feedback Due to Manipulative Insincerity
Examining case studies reveals how manipulative insincerity leads to ineffective feedback, causing significant organizational setbacks. In one tech company, a manager, fearing conflict, consistently provided vague and overly positive feedback.
This lack of candor prevented a talented but underperforming team member from recognizing and addressing crucial developmental areas. Consequently, the team members continued to underperform, ultimately impacting the team's project delivery and morale.
Another case occurred in a healthcare setting, where a senior doctor's manipulative insincerity in feedback led to a culture of complacency. The doctor avoided giving constructive criticism to junior staff, fearing it might damage their rapport.
This absence of honest feedback impeded the growth and learning of the junior staff, resulting in repeated mistakes and inefficiencies in patient care.
Overcoming the Challenges of Poor Feedback
Overcoming the challenges of poor feedback in the presence of manipulative insincerity involves several key strategies.
First, establishing a culture of open and honest communication is crucial. This can be achieved by setting clear expectations for feedback and encouraging a practice of regular, candid discussions.
Training programs can also be instrumental in equipping employees with skills to give and receive constructive feedback effectively. Additionally, implementing anonymous feedback mechanisms can help in garnering honest opinions, especially in environments where direct criticism may be discouraged.
Leadership must also lead by example, demonstrating transparency and sincerity in their feedback, thereby fostering a trust-based environment where honest feedback is valued and encouraged.
Manipulative Insincerity in Different Organizational Levels
Manipulative insincerity permeates various levels of an organization, each manifesting uniquely.
At the executive level, it might appear as strategic misinformation to shareholders or the board to mask performance issues. Middle management could exhibit it through selective reporting or sugarcoating team issues to upper management.
On the front lines, employees might agree superficially with new policies while privately resisting changes.
This disparity in behavior across hierarchical levels creates a disjointed organizational culture, where true intentions and actual situations are obscured, leading to inefficient decision-making, strained interdepartmental relationships, and a general atmosphere of distrust and misalignment within the organization.
Wrapping
Manipulative insincerity, with its multifaceted manifestations across organizational levels, poses a significant threat to the health and effectiveness of any organization. It distorts communication, erodes trust, and hinders genuine feedback, ultimately impacting decision-making and overall performance.
Addressing this insidious issue requires a concerted effort to foster a culture of honesty and transparency, bolstered by strategies like Radical Candor.
By recognizing and actively countering manipulative behaviors, organizations can cultivate an environment of trust and sincerity, essential for fostering collaboration, innovation, and long-term success in today's dynamic and competitive business landscape.
Categories
Blog
(2726)
Business Management
(333)
Employee Engagement
(213)
Digital Transformation
(185)
Growth
(124)
Intranets
(121)
Remote Work
(61)
Sales
(48)
Collaboration
(43)
Culture
(29)
Project management
(29)
Customer Experience
(26)
Knowledge Management
(21)
Leadership
(20)
Comparisons
(8)
News
(1)
Ready to learn more? 👍
One platform to optimize, manage and track all of your teams. Your new digital workplace is a click away. 🚀
Free for 14 days, no credit card required.